[React.js] 리덕스(액션,미들웨어, 리듀서, 스토어)
2021. 7. 21. 01:57ㆍWeb_Programming/React

💻 리덕스 란?
상태관리 라이브러리입니다.
자세한 내용은 이전 포스팅에서 다뤘기에 생략하겠습니다.
[우아한 테크러닝 4기] redux 구현해보기
안녕하세요. 이번 포스팅에서는 제가 지금 참여하고 있는 우아한 테크러닝 4기에서 들었던 강의 내용을 다뤄보려 합니다! 이번 강의에서는 redux를 javaScript를 이용하여 간단하게 구현하면서, redux
keeper.tistory.com
이 리덕스 사용의 장점은 아래와 같습니다.
- 컴포넌트 코드로부터 상태관리 코드 분리
- 미들웨어를 이용한 다양한 기능 추가
- redux-saga
- 로컬 스토리지에 데이터 저장 및 불러오기
- SSR시 데이터 전달이 간편
리덕스 상태값은 하나의 객체로 표현가능하여, 해당 객체만 문자열로 변환하여 서버에 넘겨주어 매우 간편
- 리액트 ContextAPI 보다 효율적인 렌더링
💡 Context API vs Redux
ContextAPI
import React, { userContext, createContext, useReducer } from 'react';
// 컨텍스트
const AppContext = createContext({});
const DispatchContext = createContext(() => {});
// 루트 컴포넌트
export default function App() {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, INITIAL_STATE);
return(
<>
<AppContext.Provider value={state}>
<DispatchContext.Provider value={dispatch}>
<User />
<Product />
</DispatchContext.Provider>
</AppContext.Provider>
</>
);
}
// 리듀서
const INITIAL_STATE = {
user: {name: 'horong'},
produce: {name: 'Galaxy S20'},
}
function reducer(state, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'setUserName':
return {
...state,
user: {...state.user, name: action.name}}
}
}
User 컴포넌트 내부
// User 컴포넌트
function User() {
const { user } = useContext(AppContext);
const dispatch = useContext(DispatchContext);
return (
<>
<p>{user.name}</p>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'setUserName', name: 'hong' })}>
사용자 이름 수정
</button>
</>
)
}
// Product 컴포넌트
function Product() {
const { product } = useContext(AppContext);
return <p>{`제품 이름: ${product.name}`}</p>
}
❗ 하나의 context로 관리
👉 이러한 경우에 상태값이 하나만 바뀌어도 전체가 다시 렌더링 되는 문제 발생
👉 context API를 사용하는 경우에는 userContext / productContext 로 나눈다고 하더라도 데이터를 동적으로 다루어야 하는 경우에는 까다로움
Redux
import React from 'react';
import { createStore } from 'redux';
import { Provider, useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux';
import rootReducer from './rootReducer'
// 루트 컴포넌트
export default function App() {
return (
<>
<Provider store={store}>
<User />
<Product />
</Provider>
</>
);
}
// 리듀서
const store = createStore(rootReducer);
User 컴포넌트 내부
// User 컴포넌트
function User() {
const user = useSelector(state => state.user);
const dispatch = useDispatch();
return (
<>
<p>{user.name}</p>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'setUserName', name: 'hong' })}>
사용자 이름 수정
</button>
</>
);
}
// Product 컴포넌트
function Product() {
const product = useSelector(state => state.product);
return <p>{`제품 이름: ${product.name}`}</p>
}
❗ useContext 를 사용하던 부분을 상태값은 useSelector를 사용하고 상태값 변경함수는 useDispatch를 사용
👉 리덕스에서는 Context API를 사용하여 UserContext / ProductContex 로 나누지 않아도 렌더링이 효율적으로 동작
💻 액션, 미들웨어
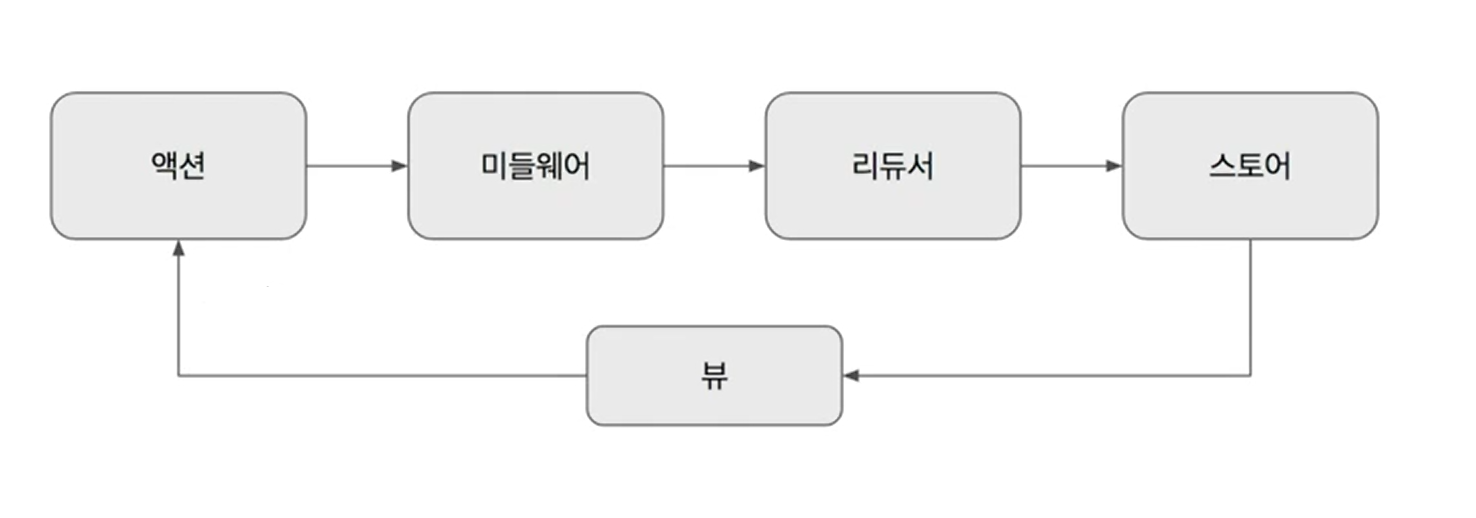
리덕스는 아래 4가지 요소가 있습니다.
- 액션 : "상태 변화를 위한 수행을 나타내는 객체"
- 미들웨어 : 액션 처리로, 여기서 여러가지 기능을 넣을 수 있습니다.
- 리듀서 : "스토어의 액션들을 수행하도록 해주는 함수"
- 스토어 : 상태 값들을 저장해두는 공간
이들은 아래와 같은 단방향 흐름의 구조를 가집니다.
뷰에서 상탯값 변경 액션을 발생
👉 미들웨어가 액션 처리
👉 리듀서에서 액션의 상태값 변경 처리 및 새로운 상태값 반환
👉 스토어에 저장
💡 액션
"상태 변화를 위한 수행을 나타내는 객체"
아래와 같이 액션을 구분하는 type과 액션에 사용되는 데이터를 가집니다.
{ type: 'todo/ADD', title: '...' }
{ type: 'todo/REMOVE', title: '...' }
대게 액션을 정의할 떄 actioncreate함수도 같이 생성
👉 액션 생성시, 좀더 직관적으로 보여지도록 합니다.
export const ADD = 'todo/ADD';
export const REMOVE = 'todo/REMOVE';
export function addTodo({ title, priority }) {
return { type: ADD, title, priority }
}
export function removeTodo({ id }) {
return { type: REMOVE, id }
}
💡 미들웨어
미들웨어는 커링함수, 클로져함수의 형태를 가집니다.
이유는, action => next(action) 영역에서 store 와 next 를 사용하기 위함입니다.
const myMiddleware = store => next => action => next(action);
몇가지 미들웨어의 예시를 살펴보겠습니다.
🔹 상태값 변경전 후의 값을 출력
// 미들웨어
const printLog = store => next => action => {
console.log(`prev state = ${JSON.stringify(store.getState())}`);
const result = next(action);
console.log(`next state = ${JSON.stringify(store.getState())}`);
return result;
}
// 리듀서
const myReducer = (state = { name: 'horong' }, action) => {
console.log('myReducer');
switch(action.type) {
case 'someAction':
return {...state, name:'horong123'}
default:
return state;
}
return state;
}
// 스토어
const store = createStore(myReducer, applyMiddleware(printLog));
// 액션 실행
store.dispatch({ type: 'someAction' })
🔹 로컬스토리지에 저장
// 미들웨어
const saveToLocalStorage = store => next => action => {
if (action.meta?.localStorageKey) {
localStorage.setItem(action.meta?.loaclStorageKey, JSON.stringify(action));
}
return next(action);
}
// 리듀서
const myReducer = (state = { name: 'horong' }, action) => {
console.log('myReducer');
switch(action.type) {
case 'someAction':
return {...state, name:'horong123'}
default:
return state;
}
return state;
}
// 스토어
const store = createStore(myReducer, applyMiddleware(saveToLocalStorage));
// 액션 실행
store.dispatch({
type: 'someAction',
title: 'asdf',
meta: { localStorageKey: 'myKey' }
});💻 리듀서, 스토어
💡 리듀서
"스토어의 액션들을 수행하도록 해주는 함수"
액션 객체와 함께 dispatch 함수를 호출하여 리듀서 호출 가능
// 리듀서 함수
function reducer(state = INITIAL_STATE, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case REMOVE_ALL:
return {
..state,
todos: [],
};
case REMOVE:
return {
..state,
todos: state.todos.filter(todo => todo.id !== action.id),
};
default:
return state;
}
}
// 초기 상태값
const INITIAL_STATE = { todos: [] }
❗ 여기서 주의해야할 점
반환하는 state값은 아래와 같은 이유로 불변객체로 관리해야합니다.
1. state 원본 값 변경은 제어 가능하도록 createStore내에서만 변경해야함
2. 값을 이전과 비교할떄 ===연산자로 비교해햐함
+ immer 패키지
전개연산자 대신 불변객체로 관리해주는 라이브러리
import produce from 'immer';
const person = { name: 'horong', age: 22 };
const newPerson = produce(person, draft => {
draft.age = 32
})
❗ 리덕스 코드 작성시, 객체를 참조하지 말고, 객체의 고유 아이디를 참조
액션간의 객체 변경으로 새로운 객체가 생성될 경우, 값의 불일치가 일어날 수 있기 떄문
function reducer(state = INITIAL_STATE, action) {
return produce(state, draft => {
switch (action.type) {
case SET_SELECTED_PEOPLE:
draft.selectedPeople = draft.peopleList.find(
item => item.id === action.id,
);
break;
case EDIT_PEOPLE_NAME:
const people = draft.peopleList.find(
item => item.id === action.id,
);
people.name = action.name;
break;
}
})
}
❗ 리듀서 함수는 순수함수로 작성
입력이 같을 때, 같은 출력 👉 random같은 값 사용 불가
부수효과가 없어야함 👉 서버API 호출 불가
💡 리듀서 생성함수
리덕스 사용시, createReducer를 이용
👉 리듀서 맵으로 코드의 양을 줄였고, 타입 변수를 관리할 필요를 없애서 또 코드의 양을 줄인다.
import produce from 'immer';
// createReducer 정의하기
function createReducer(initialState, handlerMap) {
return function(state = initialState, action) {
return produce(state, draft => {
const handler = handlerMap[action.type];
if (handler) {
handler(draft, action);
}
})
}
}
// createReducer 사용하기
const reducer = createReducer(INITIAL_STATE, {
[ADD]: (state, action) => state.todos.push(action.todo),
[REMOVE_ALL]: state => (state.todos = []),
[REMOVE]: (state, action) => state.todos.filter(todo => todo.id !== action.id),
});
💡 스토어 생성
createSotre함수 이용하여 생성
subscibe함수를 이용하여 값변경에 대한 함수이용가능
const store = createStore(reducer);
let prevState;
store.subscribe(() => {
const state = store.getState();
if (state === prevState) {
console.log('상태값 같음');
} else {
console.log('상태값 변경됨');
}
prevState = state;
});'Web_Programming > React' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [React.js]리액트_redux-saga (0) | 2021.08.03 |
|---|---|
| [React.js]리액트 react-redux, reselect라이브러리 (0) | 2021.07.30 |
| [React.js] 리액트의 useEffect 활용법 & 성능 최적화 방법 (0) | 2021.07.19 |
| [React.js]리액트 타입선언, 조건부 렌더링, 컴포넌트 재사용성 (0) | 2021.07.16 |
| [React.js]리액트 훅 규칙, Context API, 내장 훅 (0) | 2021.07.13 |
